Wiki
- RAID 0
RAID 0 (also known as a stripe set or striped volume) splits ("stripes") data evenly across two or more disks, without parity information, redundancy, or fault tolerance. Since RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance or redundancy, the failure of one drive will cause the entire array to fail; as a result of having data striped across all disks, the failure will result in total data loss. This configuration is typically implemented having speed as the intended goal. RAID 0 is normally used to increase performance, although it can also be used as a way to create a large logical volume out of two or more physical disks.
A RAID 0 setup can be created with disks of differing sizes, but the storage space added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk. For example, if a 120 GB disk is striped together with a 320 GB disk, the size of the array will be 120 GB × 2 = 240 GB.
The diagram in this section shows how the data is distributed into Ax stripes on two disks, with A1:A2 as the first stripe, A3:A4 as the second one, etc. Once the stripe size is defined during the creation of a RAID 0 array, it needs to be maintained at all times. Since the stripes are accessed in parallel, an n-drive RAID 0 array appears as a single large disk with a data rate n times higher than the single-disk rate.
Performance
A RAID 0 array of n drives provides data read and write transfer rates up to n times higher than the individual drive rates, but with no data redundancy. As a result, RAID 0 is primarily used in applications that require high performance and are able to tolerate lower reliability, such as in scientific computing or computer gaming.
Some benchmarks of desktop applications show RAID 0 performance to be marginally better than a single drive. Another article examined these claims and concluded that "striping does not always increase performance (in certain situations it will actually be slower than a non-RAID setup), but in most situations it will yield a significant improvement in performance".[9] Synthetic benchmarks show different levels of performance improvements when multiple HDDs or SSDs are used in a RAID 0 setup, compared with single-drive performance. However, some synthetic benchmarks also show a drop in performance for the same comparison.
- RAID 1
RAID 1 consists of an exact copy (or mirror) of a set of data on two or more disks; a classic RAID 1 mirrored pair contains two disks. This configuration offers no parity, striping, or spanning of disk space across multiple disks, since the data is mirrored on all disks belonging to the array, and the array can only be as big as the smallest member disk. This layout is useful when read performance or reliability is more important than write performance or the resulting data storage capacity.
The array will continue to operate so long as at least one member drive is operational.
Performance
Any read request can be serviced and handled by any drive in the array; thus, depending on the nature of I/O load, random read performance of a RAID 1 array may equal up to the sum of each member's performance,[a] while the write performance remains at the level of a single disk. However, if disks with different speeds are used in a RAID 1 array, overall write performance is equal to the speed of the slowest disk.
Synthetic benchmarks show varying levels of performance improvements when multiple HDDs or SSDs are used in a RAID 1 setup, compared with single-drive performance. However, some synthetic benchmarks also show a drop in performance for the same comparison.
Reference Standard RAID levels
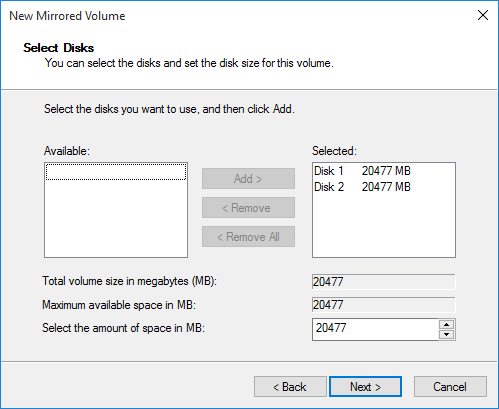
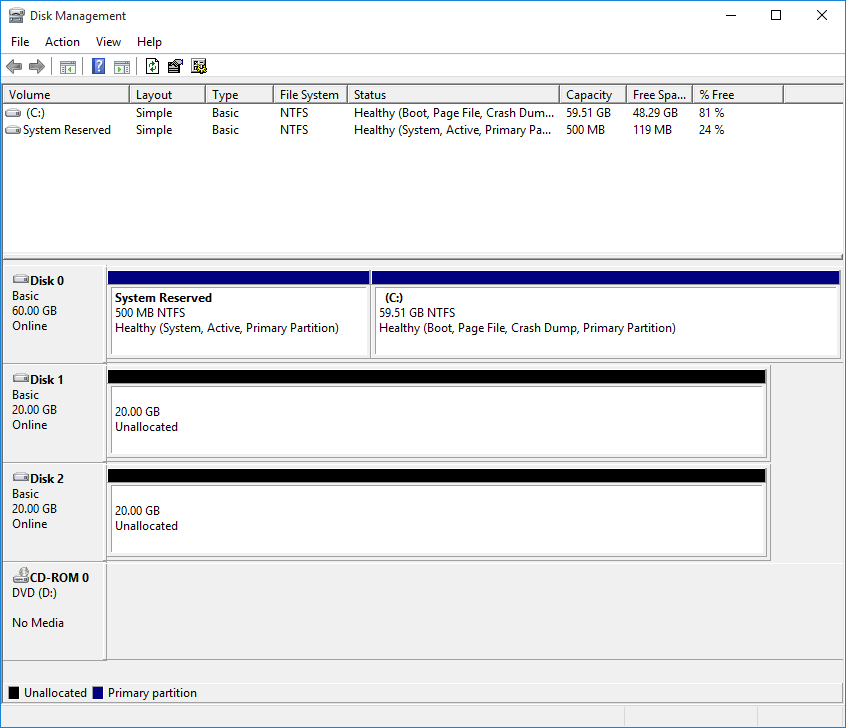
We need 2 disk to create RAID, Disk 1 and Disk 2.
Before create.
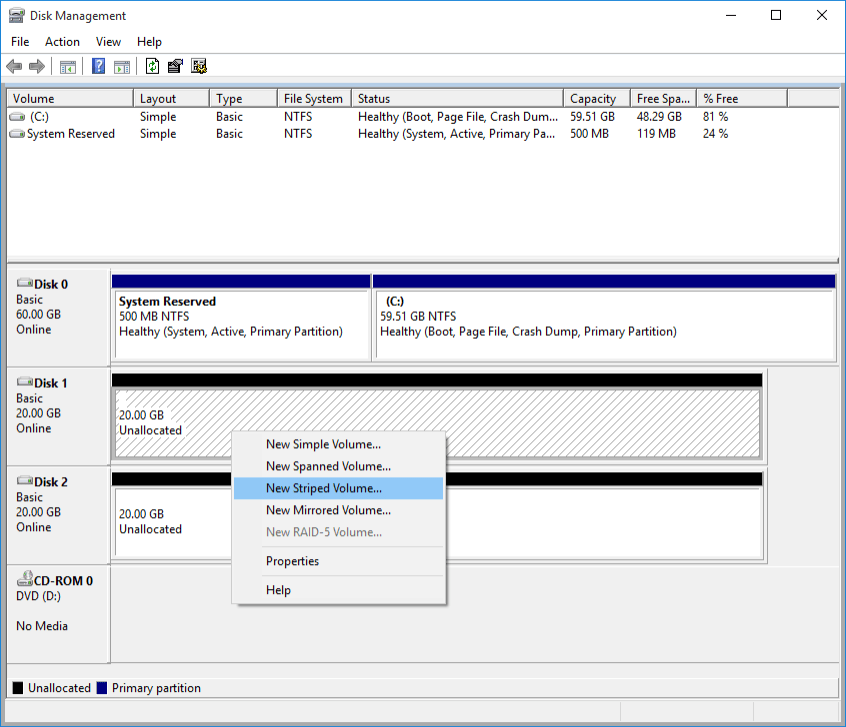
- RAID 0
Open Disk Management application, right Disk 1 → New Striped Volume...
Select Disk 2 from Available box and add it to Selected box → Next
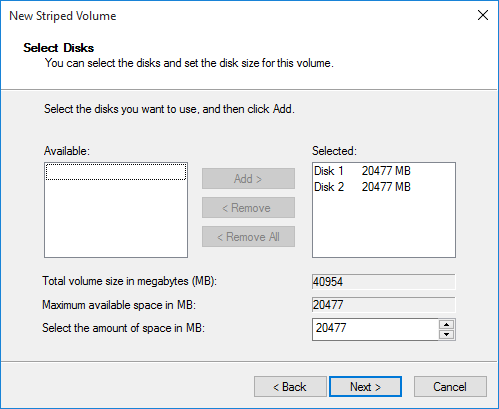
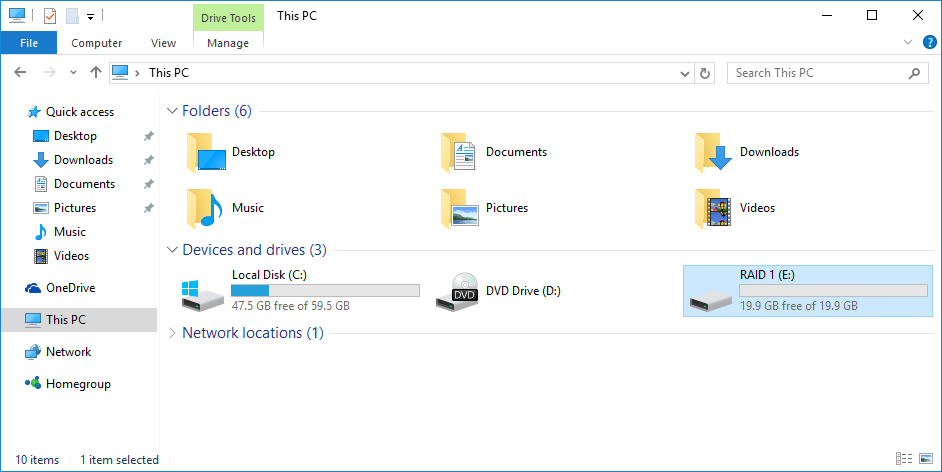
After do that
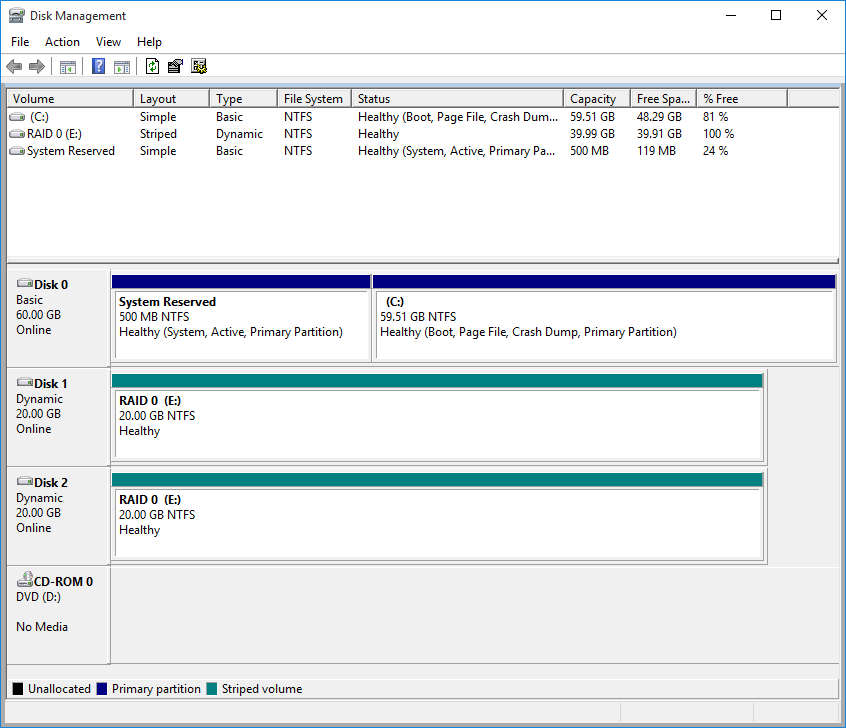
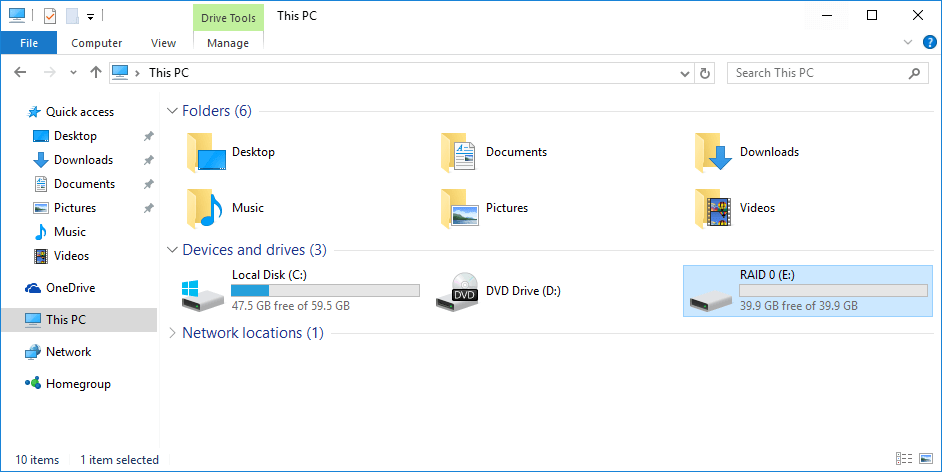
- RAID 1
Open Disk Management application, right Disk 1 → New Mirrored Volume...
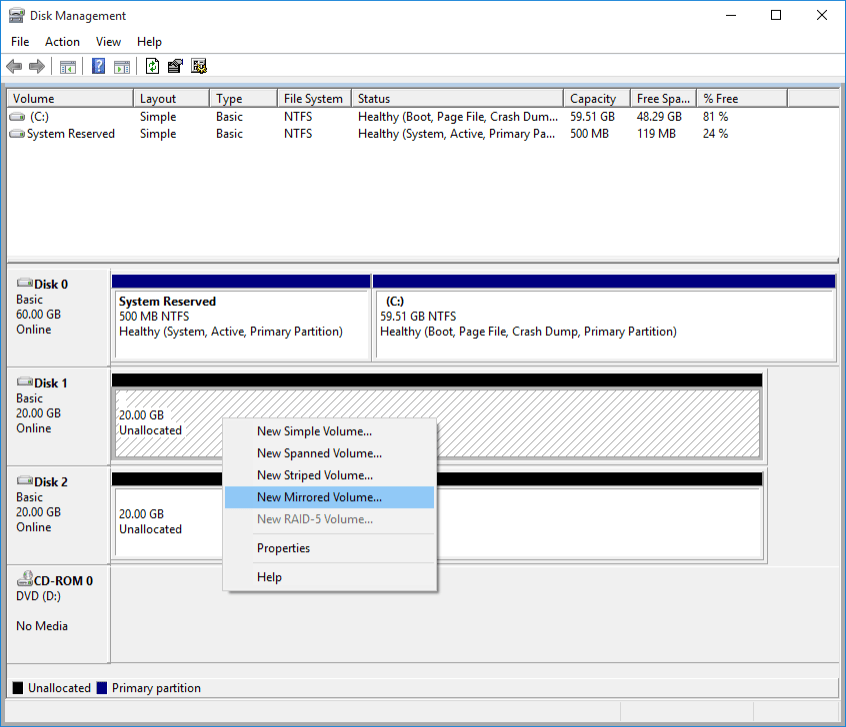
Select Disk 2 from Available box and add it to Selected box → Next
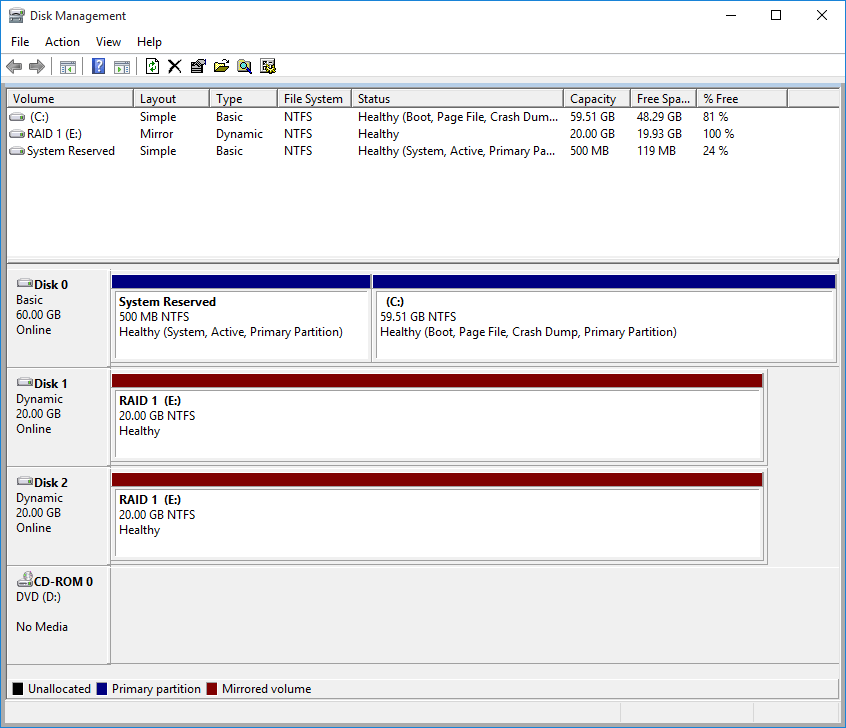
After do that