Introduction
Jenkins is an open source continuous integration tool written in Java. The project was forked from Hudson after a dispute with Oracle.
Jenkins provides continuous integration services for software development. It is a server-based system running in a servlet container such as Apache Tomcat. It supports SCM tools including AccuRev, CVS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial, Perforce, Clearcase and RTC, and can execute Apache Ant and Apache Maven based projects as well as arbitrary shell scripts and Windows batch commands. The primary developer of Jenkins is Kohsuke Kawaguchi. Released under the MIT License, Jenkins is free software.
Builds can be started by various means, including being triggered by commit in a version control system, by scheduling via a cron-like mechanism, by building when other builds have completed, and by requesting a specific build URL.
Environment and Versions
Master Ubuntu Server 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) 64-bits
172.16.136.142
Jenkins v.2.7.1
Slave Ubuntu Server 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) 64-bits
172.16.136.138
Jenkins v.2.7.1
Set date and timezone:
$ sudo apt-get install nptdate $ sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata $ sudo ntpdate pool.ntp.org
Install Jenkins on all nodes:
$ wget -q -O - https://jenkins-ci.org/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key | sudo apt-key add - $ sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list' $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install jenkins
Setup jenkins user password on slave node:
$ sudo passwd jenkins
Configuration Jenkins via Web UI on all nodes:
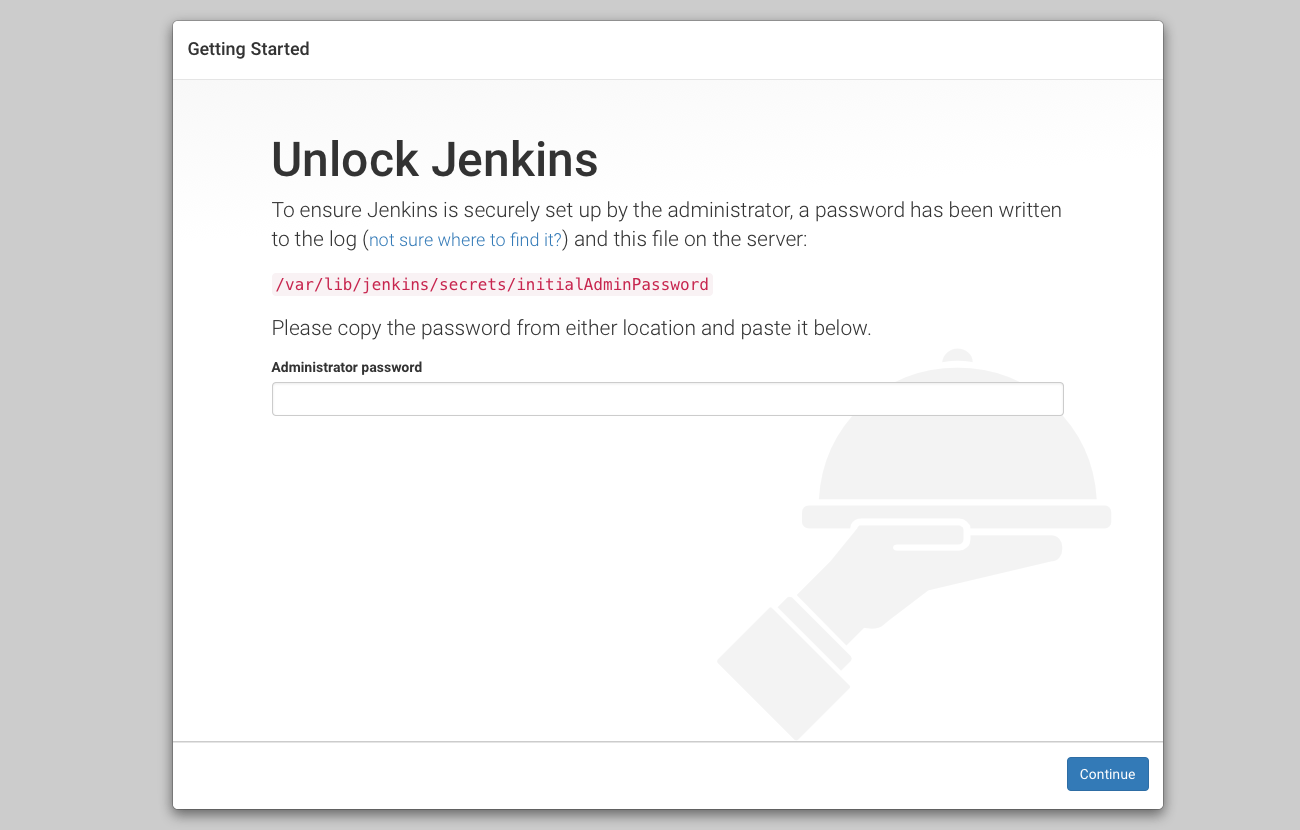
Unlock Jenkins
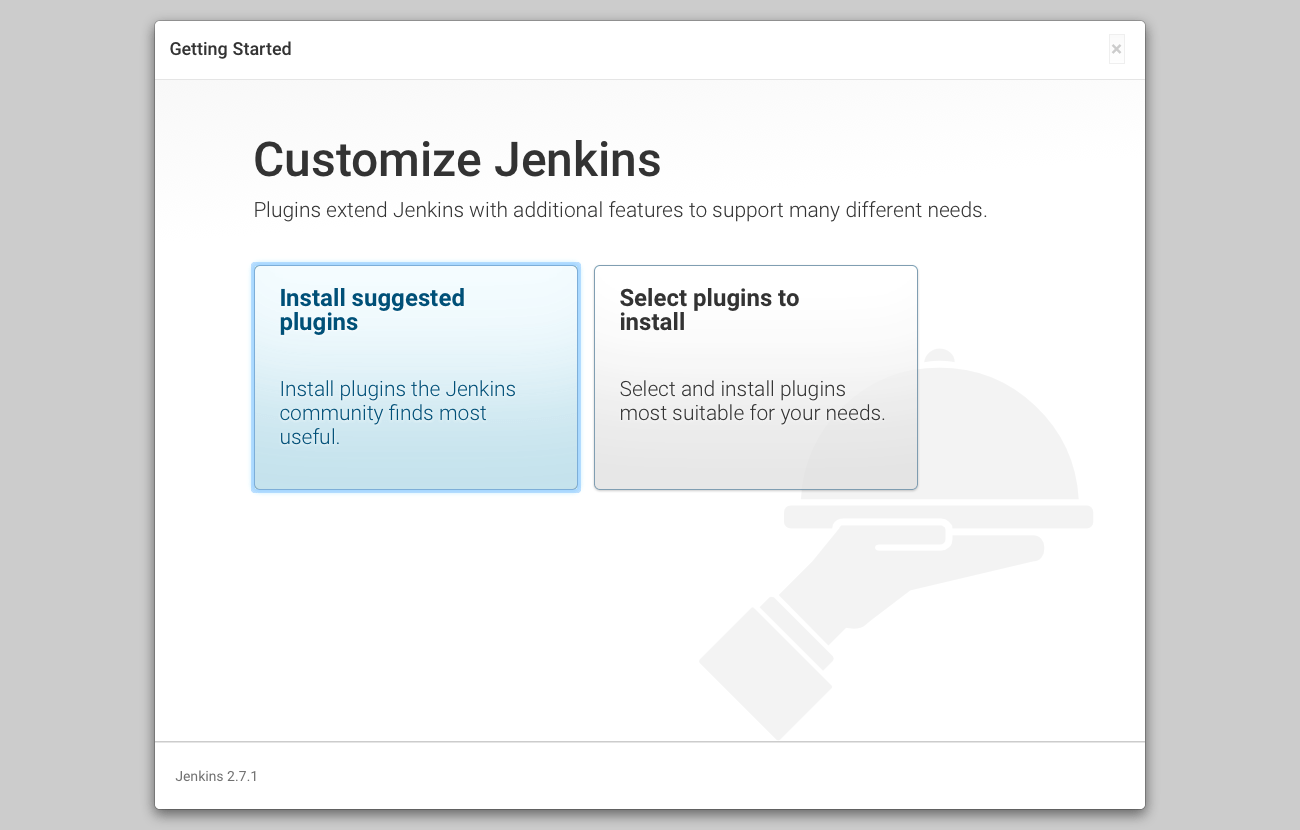
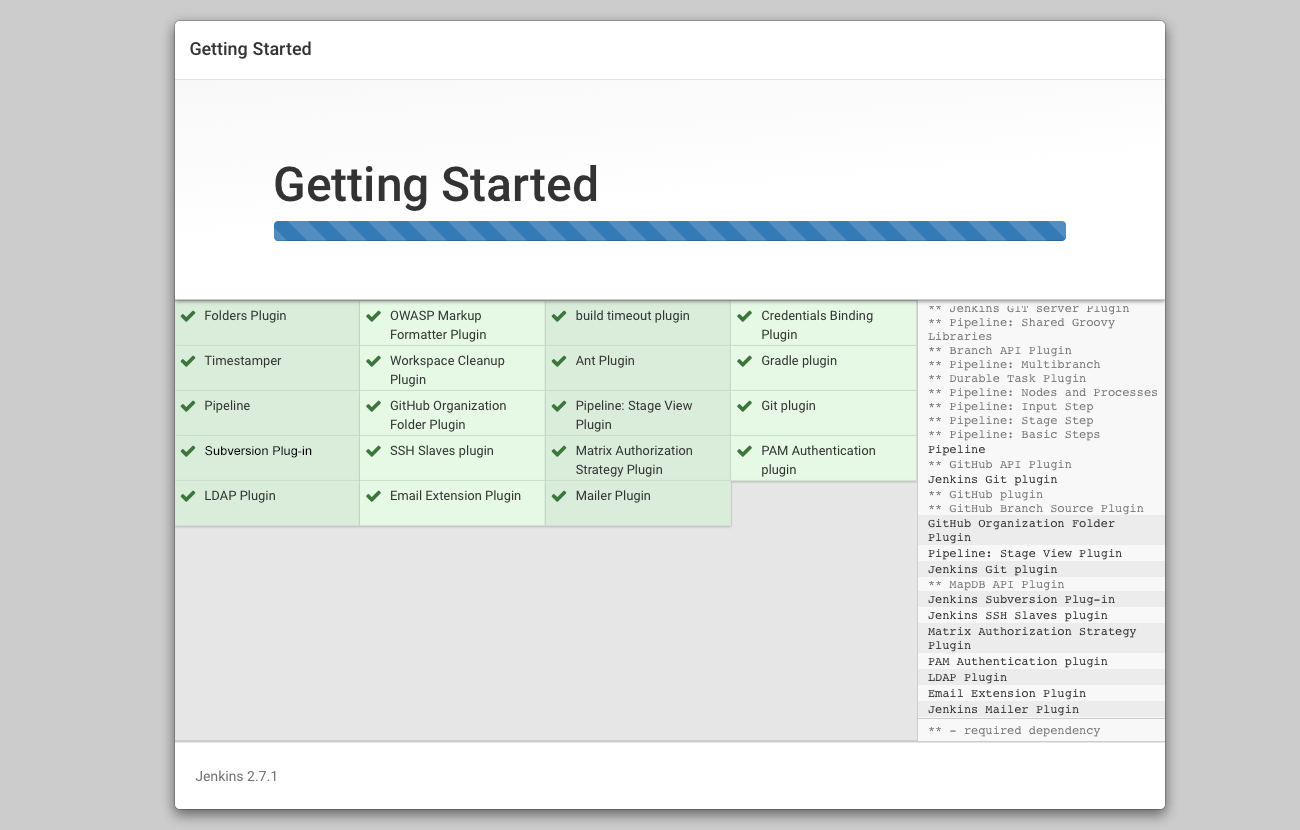
Install suggested plugins
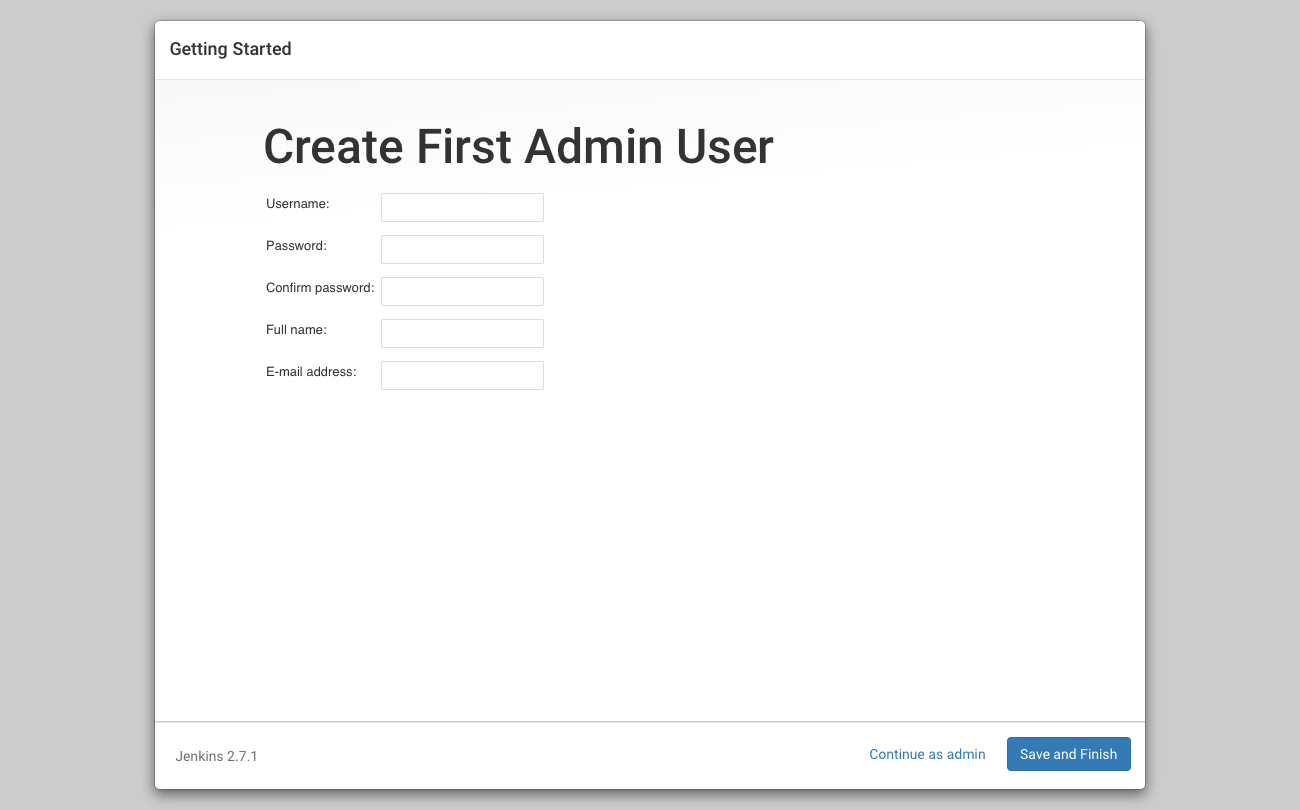
Create first admin user
Slave nodes configuration on master node:
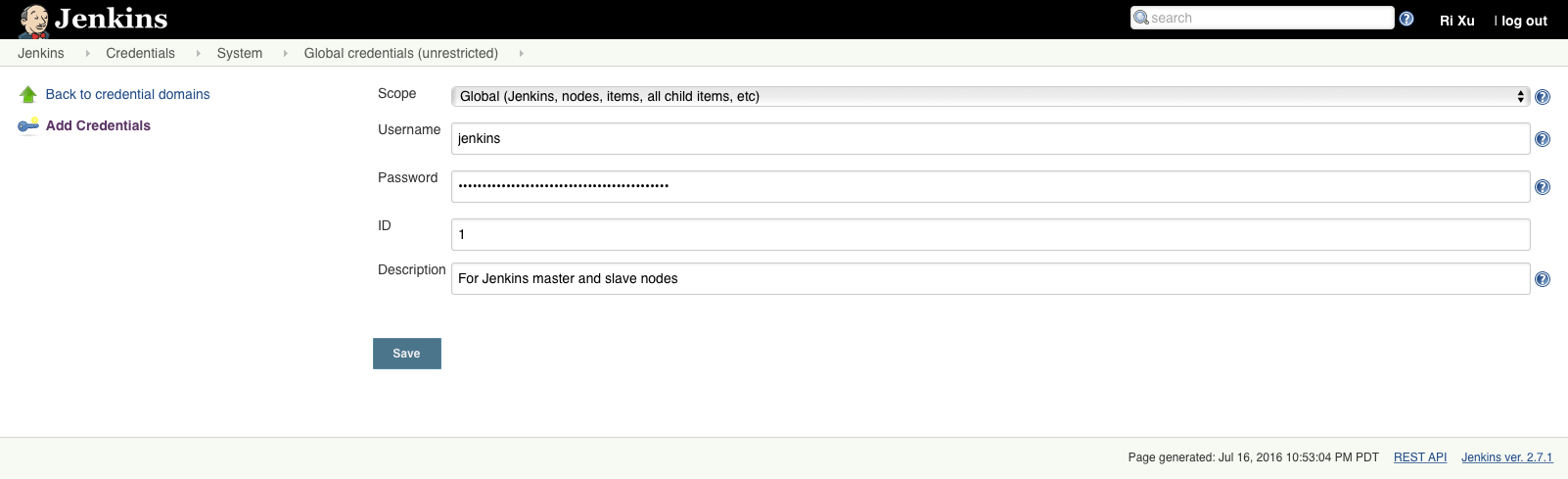
Enter Jenkins → Credentials → System → Global credentials (unrestricted) → Add Credentials
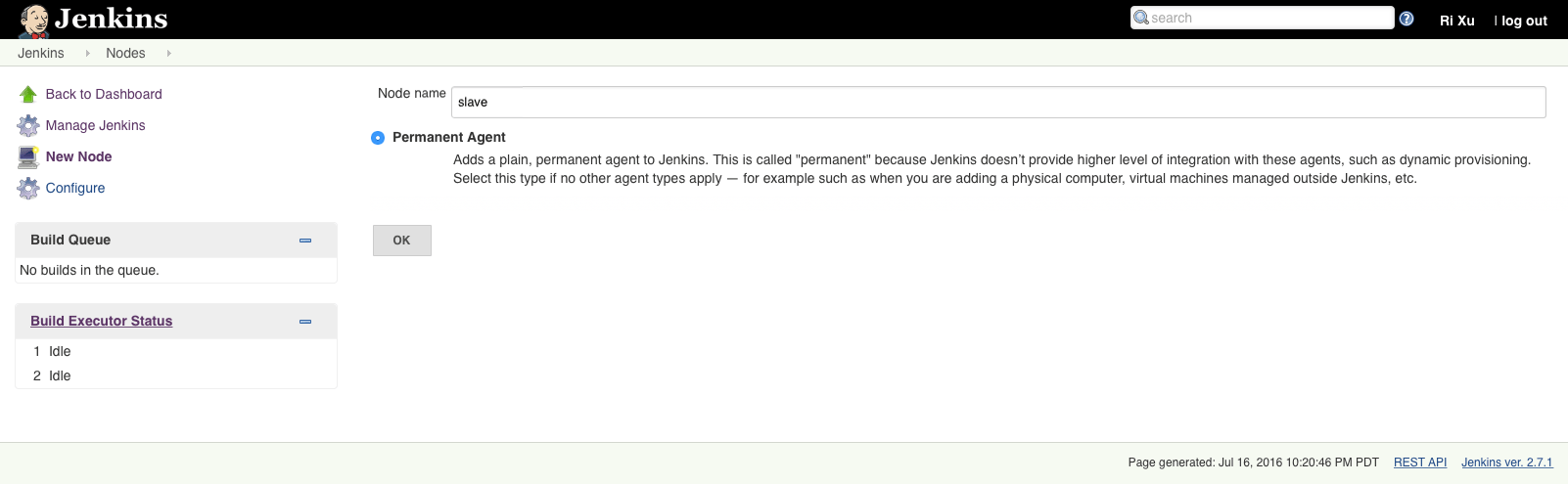
Add slave nodes:
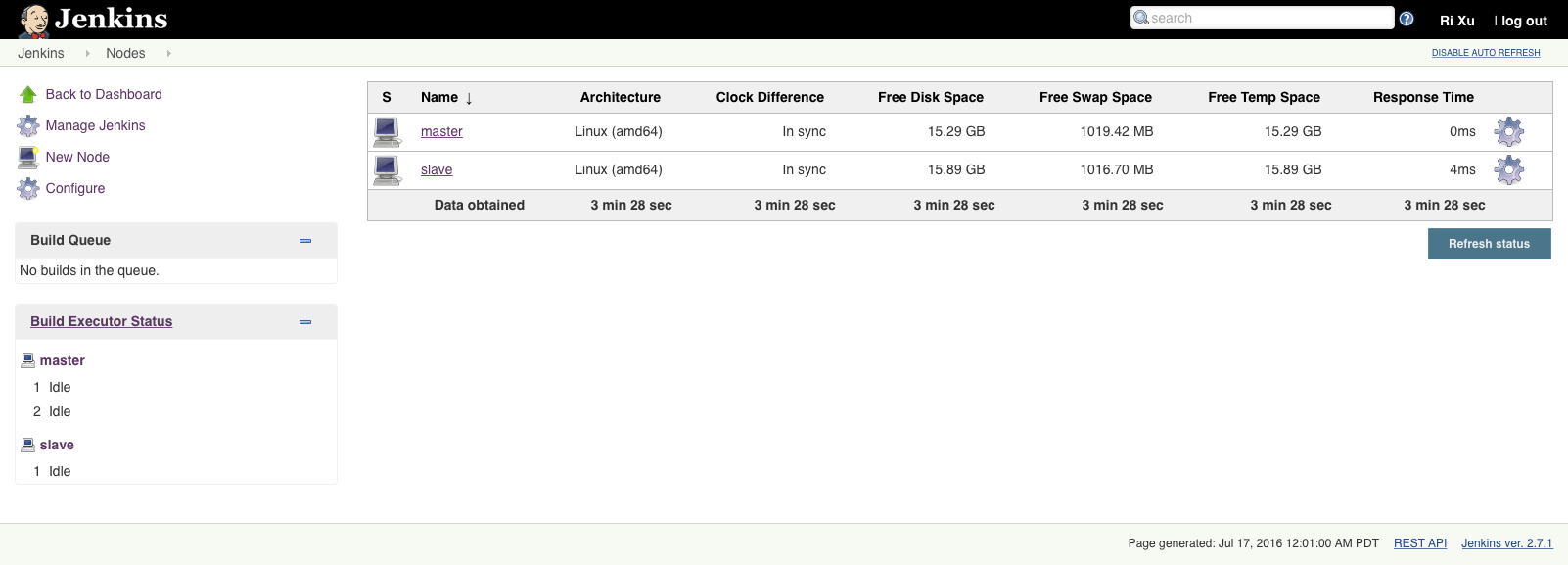
Jenkins → Manage Jenkins → New Node
Slave node configurations:
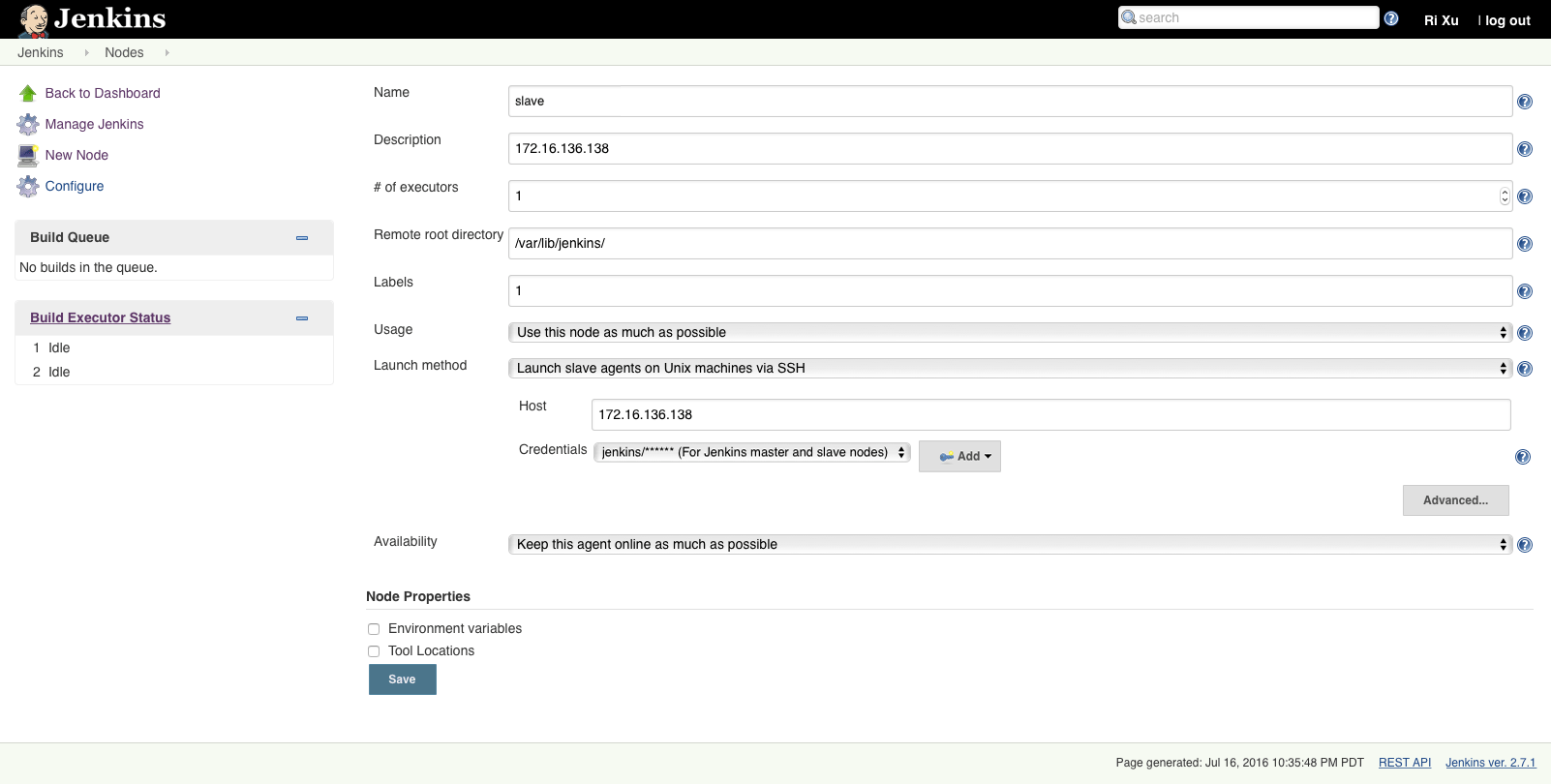
Launch slave agent
Jenkins → Nodes → slave → Launch agent