Cell
RichTextRun directly maps the settings of the rich text run.
type RichTextRun struct {
Font *Font
Text string
}
HyperlinkOpts can be passed to SetCellHyperlink to set optional hyperlink attributes (e.g. text to display and screen tip text).
type HyperlinkOpts struct {
Display *string
Tooltip *string
}
FormulaOpts can be passed to SetCellFormula to use other formula types.
type FormulaOpts struct {
Type *string // Formula type
Ref *string // Shared formula reference
}
Set cell value
func (f *File) SetCellValue(sheet, cell string, value interface{}) error
SetCellValue provides a function to set the value of a cell. This function is concurrency safe. The specified coordinates should not be in the first row of the table, a complex number can be set with string text. The following shows the supported data types:
| Supported data types |
|---|
| int |
| int8 |
| int16 |
| int32 |
| int64 |
| uint |
| uint8 |
| uint16 |
| uint32 |
| uint64 |
| float32 |
| float64 |
| string |
| []byte |
| time.Duration |
| time.Time |
| bool |
| nil |
Note that default date format is m/d/yy h:mm of time.Time type value. You can set numbers format by the SetCellStyle function. If you need to set the specialized date in Excel like January 0, 1900 or February 29, 1900, these times can not representation in Go language time.Time data type. Please set the cell value as number 0 or 60, then create and bind the date-time number format style for the cell.
Set boolean value
func (f *File) SetCellBool(sheet, cell string, value bool) error
SetCellBool provides a function to set the bool type value of a cell by given worksheet name, cell reference, and cell value.
Set RAW value
func (f *File) SetCellDefault(sheet, cell, value string) error
SetCellDefault provides a function to set the string type value of a cell as a default format without escaping the cell.
Set integer value
func (f *File) SetCellInt(sheet, cell string, value int64) error
SetCellInt provides a function to set the int64 type value of a cell by given worksheet name, cell reference, and cell value.
Set unsigned integer value
func (f *File) SetCellUint(sheet, cell string, value uint64) error
SetCellUint provides a function to set unsigned integer data type value of a cell by given worksheet name, cell reference and cell value.
Set floating point value
func (f *File) SetCellFloat(sheet, cell string, value float64, precision, bitSize int) error
SetCellFloat sets a floating point value into a cell. The precision parameter specifies how many places after the decimal will be shown while -1 is a special value that will use as many decimal places as necessary to represent the number. bitSize is 32 or 64 depending on if a float32 or float64 was originally used for the value.
Set string value
func (f *File) SetCellStr(sheet, cell, value string) error
SetCellStr provides a function to set the string type value of a cell. The total number of characters that a cell can contain 32767 characters.
Set cell style
func (f *File) SetCellStyle(sheet, topLeftCell, bottomRightCell string, styleID int) error
SetCellStyle provides a function to add style attribute for cells by given worksheet name, range reference and style ID. This function is concurrency safe. Style indexes can be obtained with the NewStyle function. Note that diagonalDown and diagonalUp type border should use the same color in the same range. SetCellStyle will overwrite the existing styles for the cell, it won't append or merge style with existing styles.
- Example 1, create borders of cell
D7onSheet1:
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Border: []excelize.Border{
{Type: "left", Color: "0000FF", Style: 3},
{Type: "top", Color: "00FF00", Style: 4},
{Type: "bottom", Color: "FFFF00", Style: 5},
{Type: "right", Color: "FF0000", Style: 6},
{Type: "diagonalDown", Color: "A020F0", Style: 8},
{Type: "diagonalUp", Color: "A020F0", Style: 8},
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
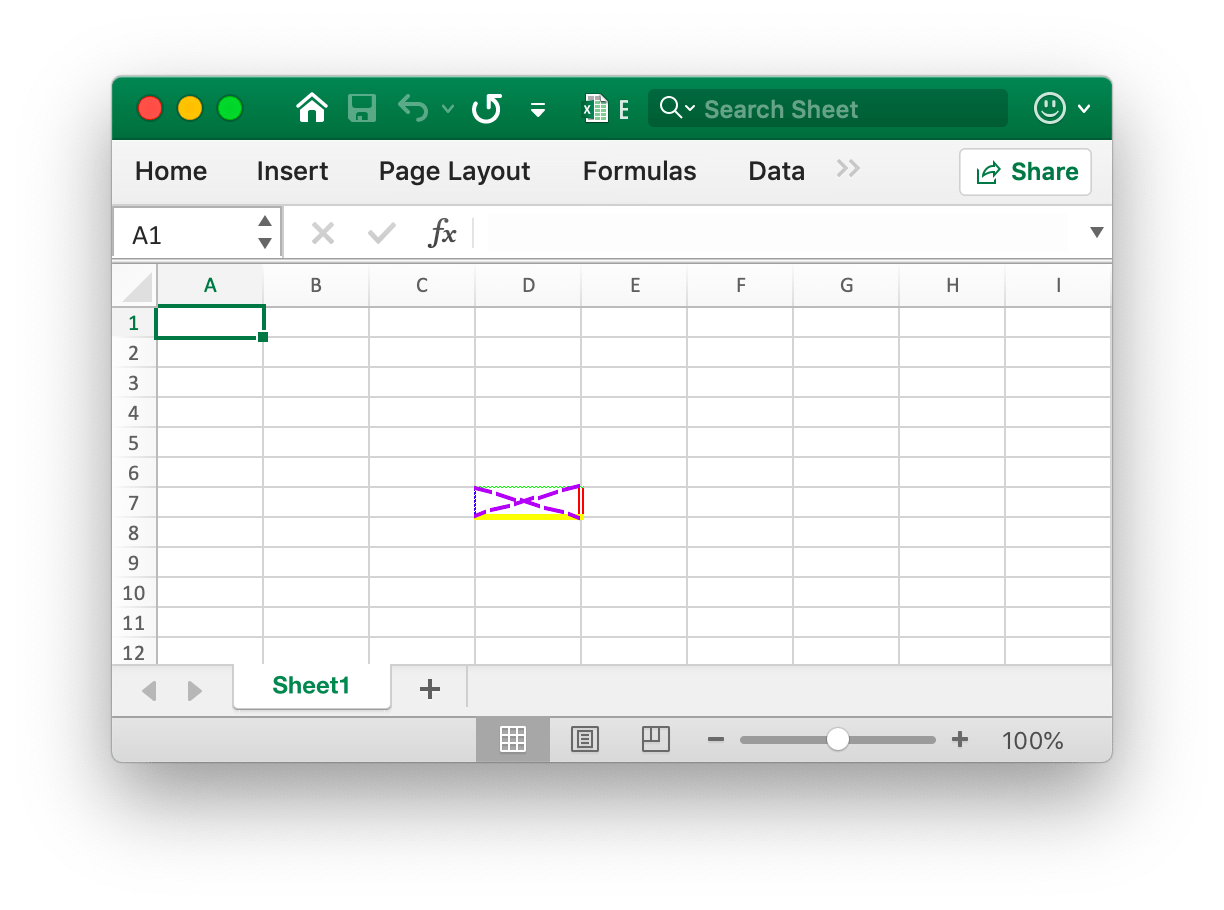
The four borders of the cell D7 are set with different styles and colors. This is related to the parameters when calling the NewStyle function. You need to set different styles to refer to the documentation for that chapter.
- Example 2, setting the gradient style for the worksheet
D7cell namedSheet1:
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Fill: excelize.Fill{Type: "gradient", Color: []string{"FFFFFF", "E0EBF5"}, Shading: 1},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
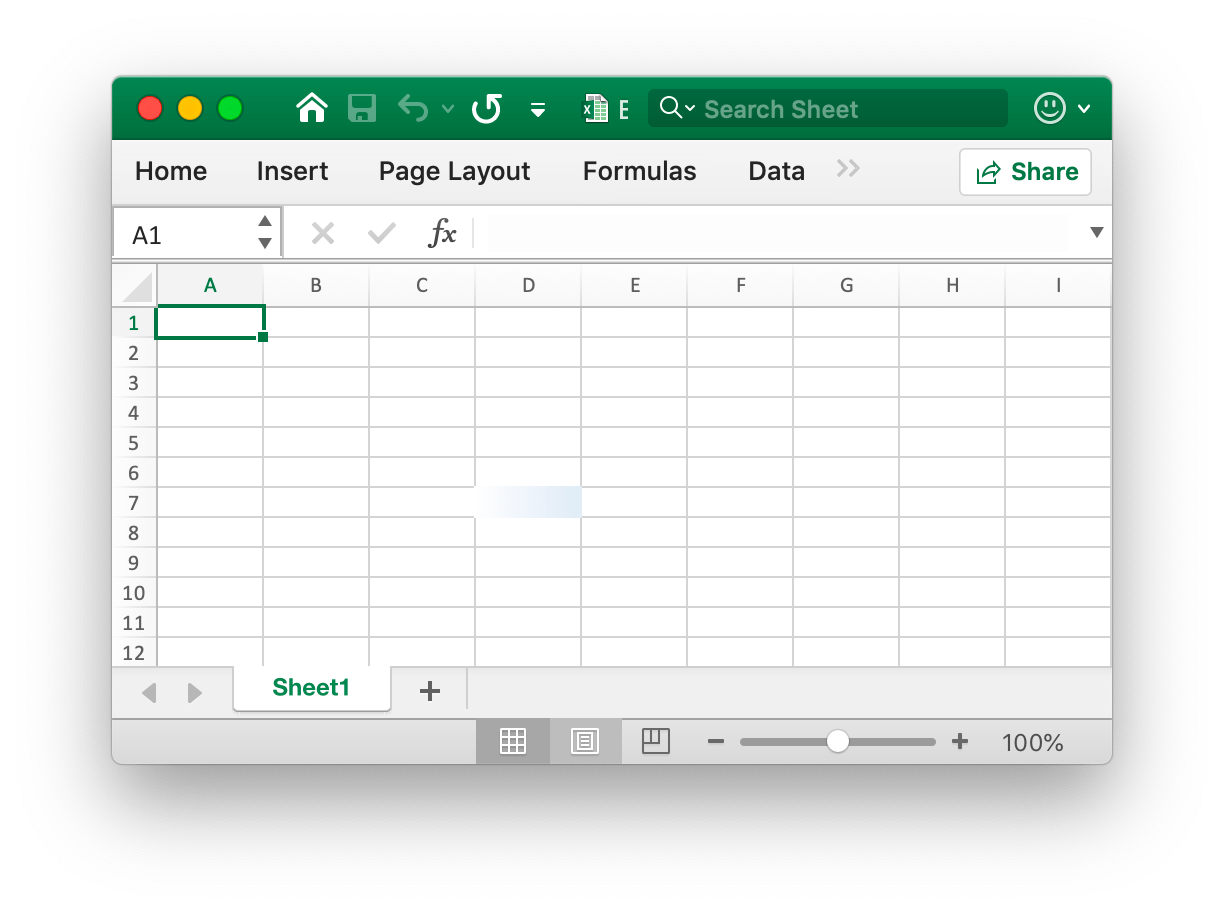
The cell D7 is set with the color fill of the gradient effect. The gradient fill effect is related to the parameter when the NewStyle function is called. You need to set different styles to refer to the documentation of this chapter.
- Example 3, set a solid fill for the
D7cell namedSheet1:
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Fill: excelize.Fill{Type: "pattern", Color: []string{"E0EBF5"}, Pattern: 1},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
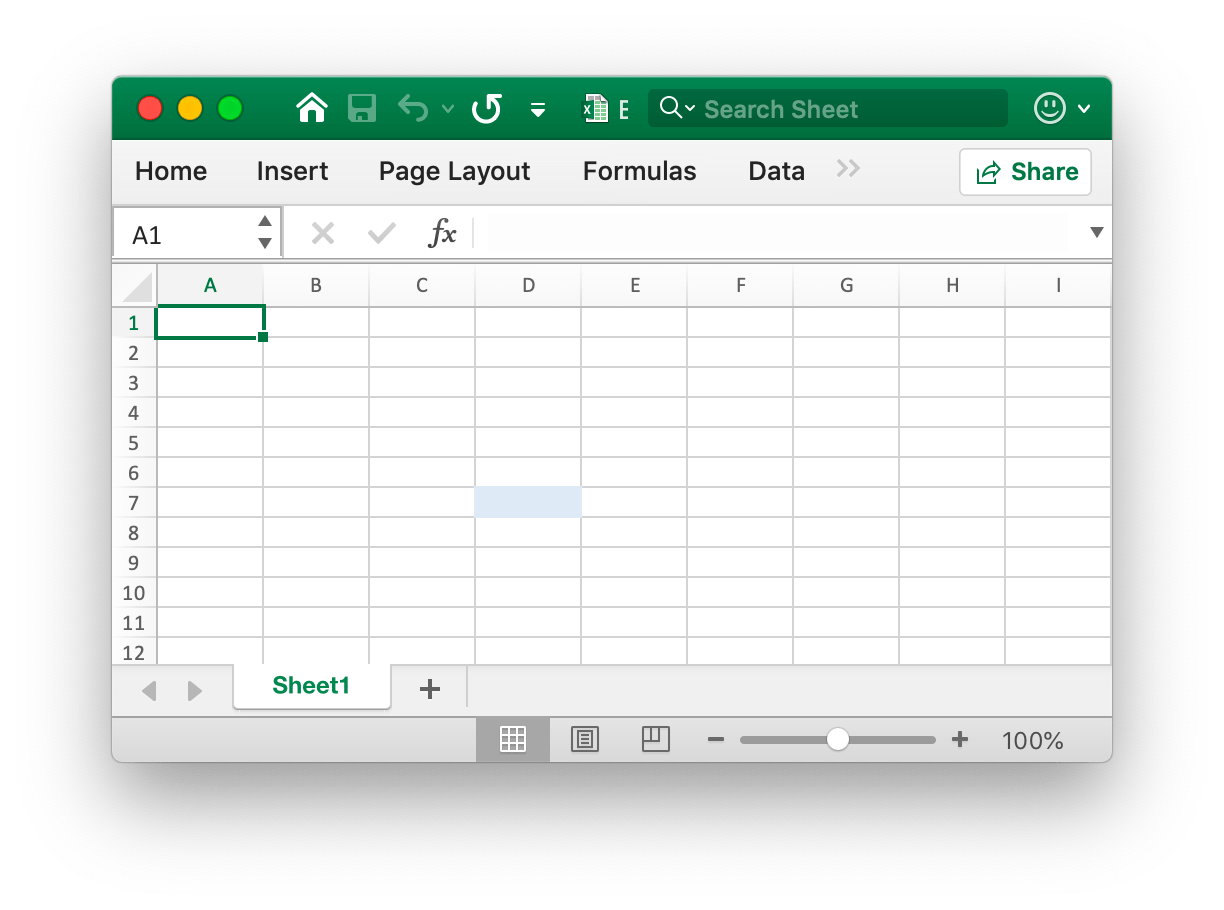
The cell D7 is set with a solid fill.
- Example 4, set the character spacing and rotation angle for the
D7cell namedSheet1:
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "D7", "Style")
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Alignment: &excelize.Alignment{
Horizontal: "center",
Indent: 1,
JustifyLastLine: true,
ReadingOrder: 0,
RelativeIndent: 1,
ShrinkToFit: true,
TextRotation: 45,
Vertical: "",
WrapText: true,
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
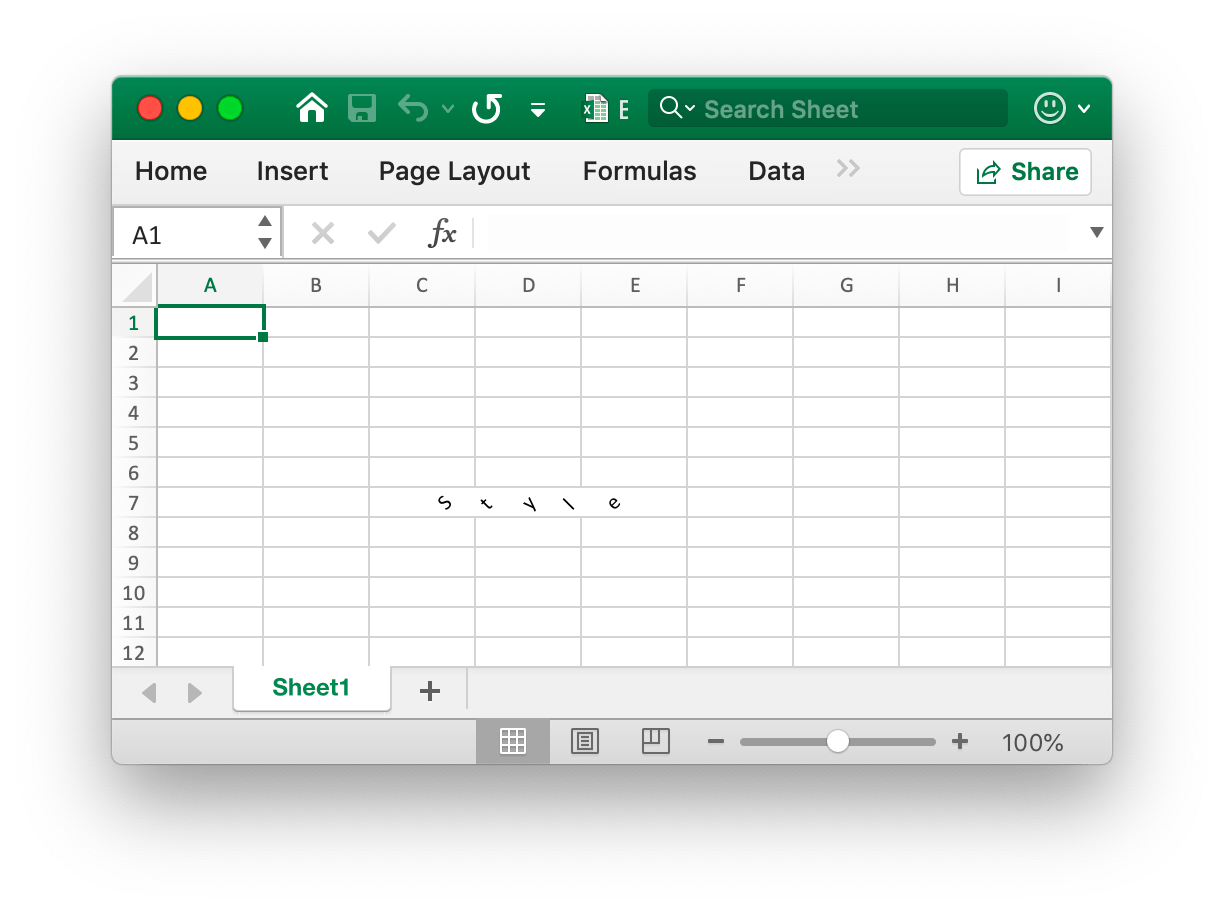
- Example 5, the date and time in Excel are represented by real numbers, for example
2017/7/4 12:00:00 PMcan be represented by the number42920.5. Set the time format for the worksheetD7cell namedSheet1:
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "D7", 42920.5)
f.SetColWidth("Sheet1", "D", "D", 13)
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{NumFmt: 22})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
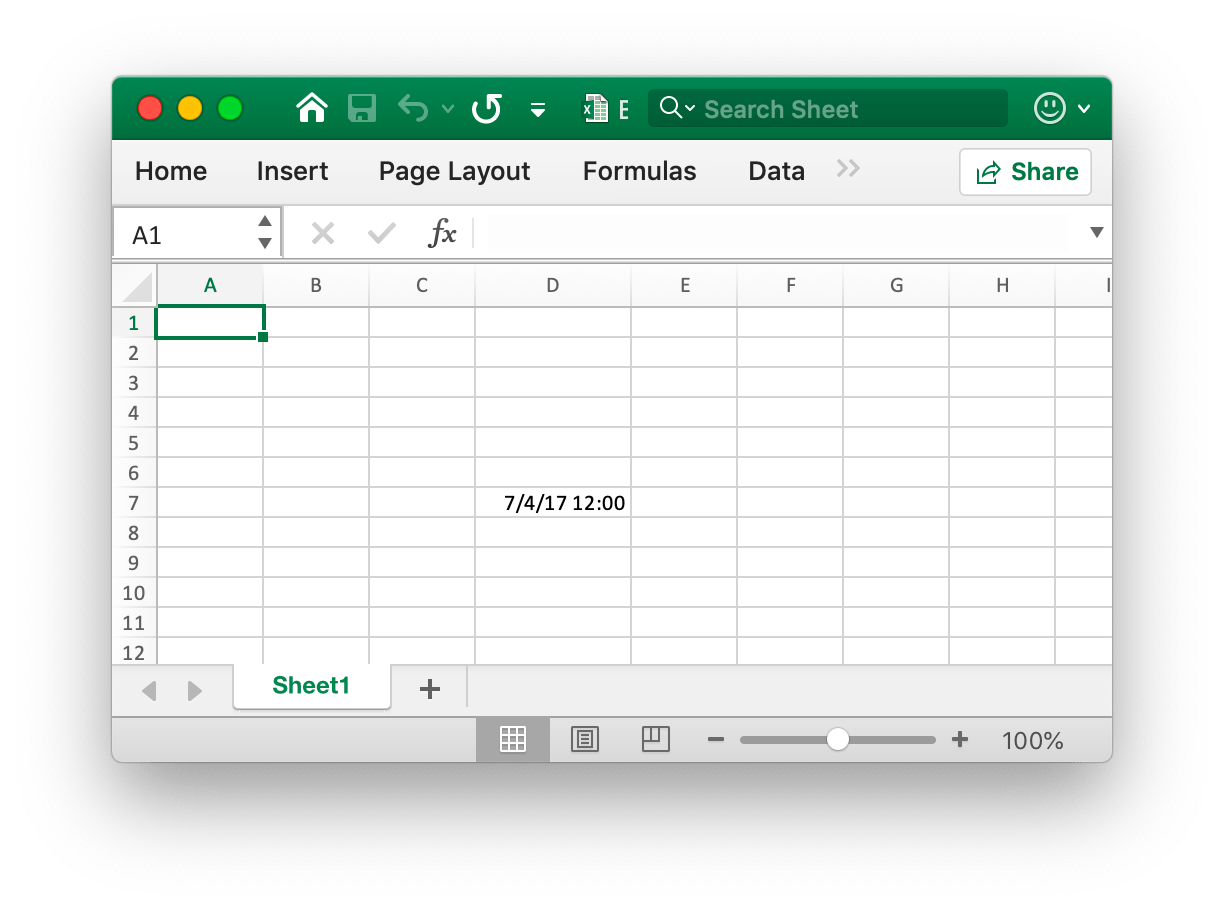
The cell D7 is set to the time format. Note that when the cell width with the time format applied is too narrow to be fully displayed, it will be displayed as ####, you can drag and drop the column width or set the column to the appropriate size by calling the SetColWidth function to make it normal display.
- Example 6, setting the font, font size, color, and skew style for the worksheet
D7cell namedSheet1:
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "D7", "Excel")
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Font: &excelize.Font{
Bold: true,
Italic: true,
Family: "Times New Roman",
Size: 36,
Color: "777777",
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
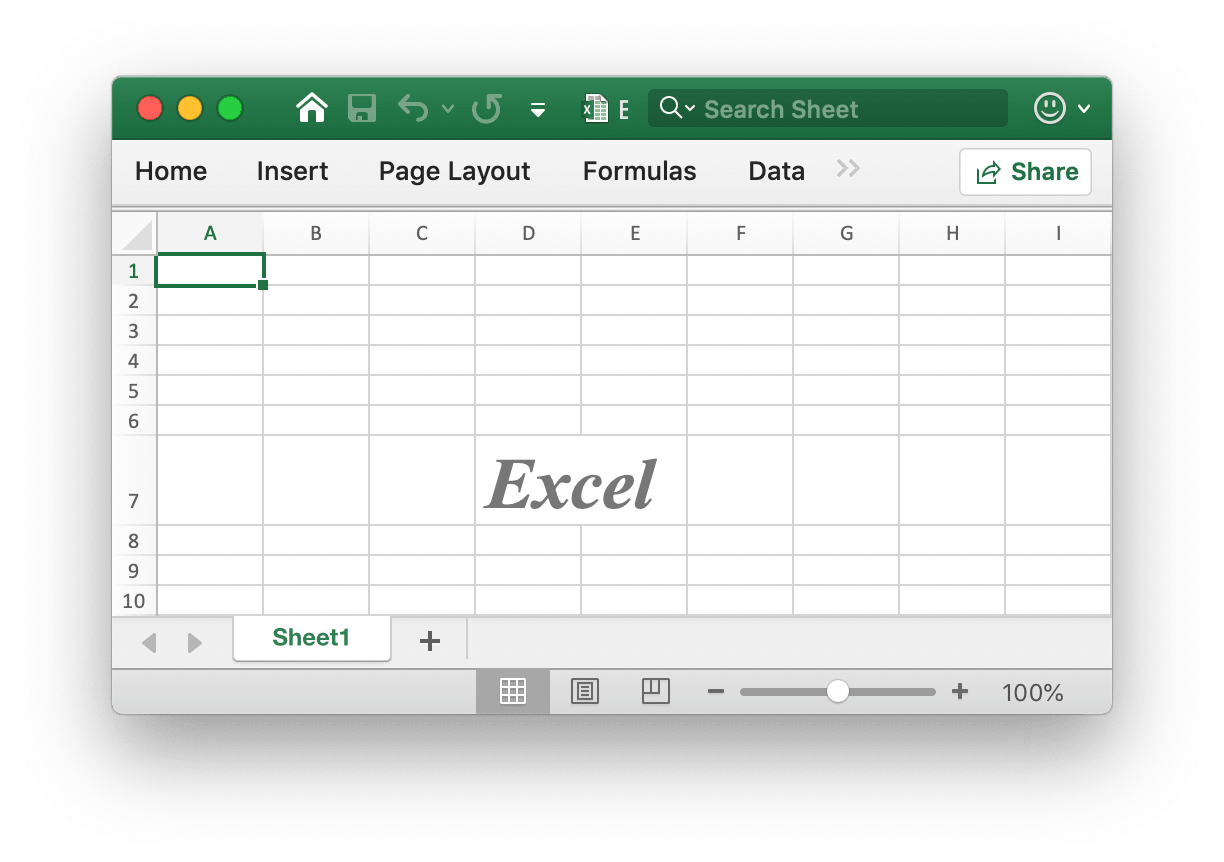
- Example 7, locking and hiding the worksheet
D7cell namedSheet1:
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Protection: &excelize.Protection{
Hidden: true,
Locked: true,
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "D7", "D7", style)
To lock a cell or hide a formula, protect the worksheet. On the "Review" tab, click "Protect Worksheet".
Set hyperlink
func (f *File) SetCellHyperLink(sheet, cell, link, linkType string, opts ...HyperlinkOpts) error
SetCellHyperLink provides a function to set cell hyperlinks by given worksheet name and link URL address. LinkType defines two types of hyperlinks External for the website or Location for moving to one of the cells in this workbook. The maximum limit of hyperlinks in a worksheet is 65530. This function is only used to set the hyperlink of the cell and doesn't affect the value of the cell. If you need to set the value of the cell, please use the other functions such as SetCellStyle or SetSheetRow. Below is an example of an external link.
- Example 1, adding an external link to the
A3cell of the worksheet namedSheet1:
display, tooltip := "https://github.com/xuri/excelize", "Excelize on GitHub"
if err := f.SetCellHyperLink("Sheet1", "A3",
"https://github.com/xuri/excelize", "External", excelize.HyperlinkOpts{
Display: &display,
Tooltip: &tooltip,
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Set the font and underline style for the cell
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Font: &excelize.Font{Color: "1265BE", Underline: "single"},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
err = f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "A3", "A3", style)
- Example 2, adding an internal location link to the
A3cell namedSheet1:
err := f.SetCellHyperLink("Sheet1", "A3", "Sheet1!A40", "Location")
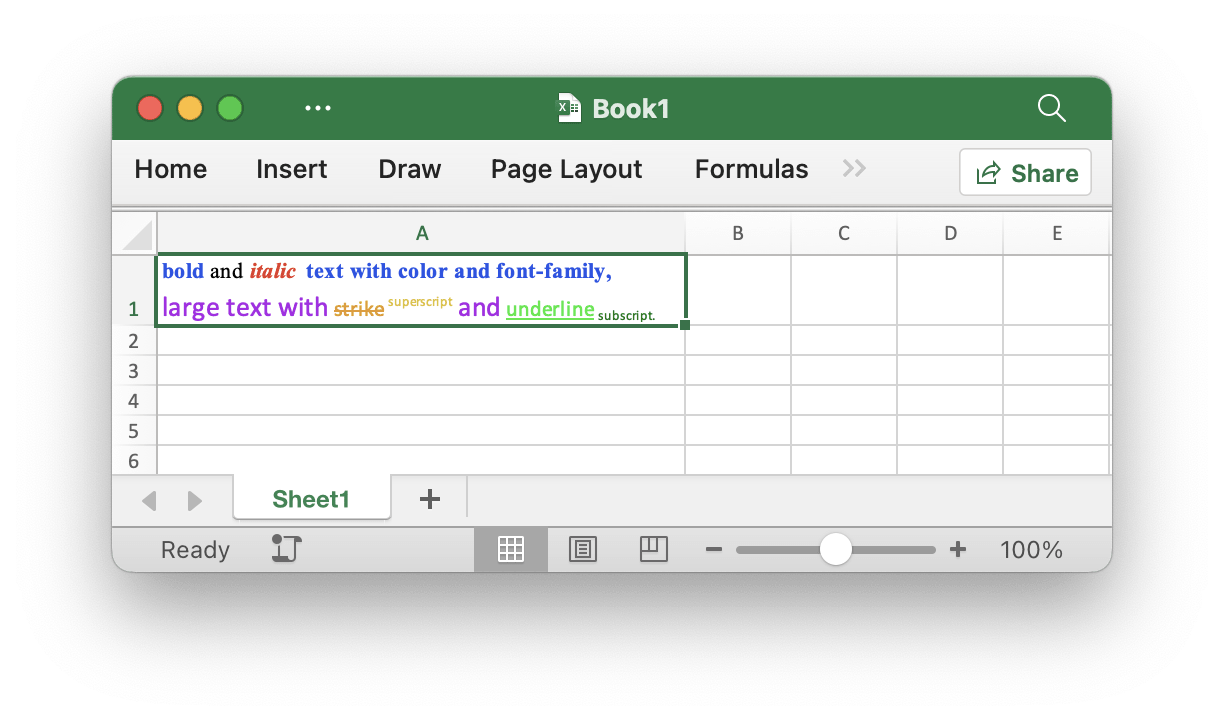
Set cell rich text
func (f *File) SetCellRichText(sheet, cell string, runs []RichTextRun) error
SetCellRichText provides a function to set a cell with rich text by given worksheet.
For example, set rich text on the A1 cell of the worksheet named Sheet1:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
if err := f.SetRowHeight("Sheet1", 1, 35); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err := f.SetColWidth("Sheet1", "A", "A", 44); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err := f.SetCellRichText("Sheet1", "A1", []excelize.RichTextRun{
{
Text: "bold",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Bold: true,
Color: "2354E8",
Family: "Times New Roman",
},
},
{
Text: " and ",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Family: "Times New Roman",
},
},
{
Text: "italic ",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Bold: true,
Color: "E83723",
Italic: true,
Family: "Times New Roman",
},
},
{
Text: "text with color and font-family,",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Bold: true,
Color: "2354E8",
Family: "Times New Roman",
},
},
{
Text: "\r\nlarge text with ",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Size: 14,
Color: "AD23E8",
},
},
{
Text: "strike",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Color: "E89923",
Strike: true,
},
},
{
Text: " superscript",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Color: "DBC21F",
VertAlign: "superscript",
},
},
{
Text: " and ",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Size: 14,
Color: "AD23E8",
VertAlign: "baseline",
},
},
{
Text: "underline",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Color: "23E833",
Underline: "single",
},
},
{
Text: " subscript.",
Font: &excelize.Font{
Color: "017505",
VertAlign: "subscript",
},
},
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
style, err := f.NewStyle(&excelize.Style{
Alignment: &excelize.Alignment{
WrapText: true,
},
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err := f.SetCellStyle("Sheet1", "A1", "A1", style); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err := f.SaveAs("Book1.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
Get cell rich text
func (f *File) GetCellRichText(sheet, cell string) ([]RichTextRun, error)
GetCellRichText provides a function to get the rich text of cells by given worksheet.
Get cell value
func (f *File) GetCellValue(sheet, cell string, opts ...Options) (string, error)
GetCellValue provides a function to get formatted value from cell by given worksheet name and cell reference in spreadsheet. The return value is converted to the string type. This function is concurrency safe. If the cell format can be applied to the value of a cell, the applied value will be returned, otherwise the original value will be returned. All cells' values will be the same in a merged range.
Get cell type
func (f *File) GetCellType(sheet, cell string) (CellType, error)
GetCellType provides a function to get the cell's data type by given worksheet name and cell reference in spreadsheet file.
Get all cell value by cols
func (f *File) GetCols(sheet string, opts ...Options) ([][]string, error)
GetCols gets the value of all cells by columns on the worksheet based on the given worksheet name, returned as a two-dimensional array, where the value of the cell is converted to the string type. If the cell format can be applied to the value of the cell, the applied value will be used, otherwise the original value will be used.
For example, get and traverse the value of all cells by columns on a worksheet named Sheet1:
cols, err := f.GetCols("Sheet1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
for _, col := range cols {
for _, rowCell := range col {
fmt.Print(rowCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
Get all cell value by rows
func (f *File) GetRows(sheet string, opts ...Options) ([][]string, error)
GetRows return all the rows in a sheet by given worksheet name, returned as a two-dimensional array, where the value of the cell is converted to the string type. If the cell format can be applied to the value of the cell, the applied value will be used, otherwise the original value will be used. GetRows fetched the rows with value or formula cells, the continually blank cells in the tail of each row will be skipped, so the length of each row may be inconsistent.
For example, get and traverse the value of all cells by rows on a worksheet named Sheet1:
rows, err := f.GetRows("Sheet1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
for _, row := range rows {
for _, colCell := range row {
fmt.Print(colCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
Get hyperlink
func (f *File) GetCellHyperLink(sheet, cell string) (bool, string, error)
GetCellHyperLink gets a cell hyperlink based on the given worksheet name and cell reference. If the cell has a hyperlink, it will return true and the link address, otherwise it will return false and an empty link address.
For example, get a hyperlink to a H6 cell on a worksheet named Sheet1:
link, target, err := f.GetCellHyperLink("Sheet1", "H6")
Get style index
func (f *File) GetCellStyle(sheet, cell string) (int, error)
The cell style index is obtained from the given worksheet name and cell reference, and the obtained index can be used as a parameter to call the SetCellValue function when copying the cell style.
Merge cells
func (f *File) MergeCell(sheet, topLeftCell, bottomRightCell string) error
MergeCell provides a function to merge cells by given range reference and sheet name. Merging cells only keeps the upper-left cell value, and discards the other values. For example, merge cells in the D3:E9 area on a worksheet named Sheet1:
err := f.MergeCell("Sheet1", "D3", "E9")
If you create a merged cell that overlaps with another existing merged cell, those merged cells that already exist will be removed.
Unmerge cells
func (f *File) UnmergeCell(sheet, topLeftCell, bottomRightCell string) error
UnmergeCell provides a function to unmerge a given range reference. For example unmerge area D3:E9 on Sheet1:
err := f.UnmergeCell("Sheet1", "D3", "E9")
Attention: overlapped areas will also be unmerged.
Get merge cells
GetMergeCells provides a function to get all merged cells from a specific worksheet.
func (f *File) GetMergeCells(sheet string) ([]MergeCell, error)
Get merged cell value
func (m *MergeCell) GetCellValue() string
GetCellValue returns merged cell value.
Get the top left cell reference of merged range
func (m *MergeCell) GetStartAxis() string
GetStartAxis returns the top left cell reference of merged range, for example: C2.
Get the bottom right cell reference of merged range
func (m *MergeCell) GetEndAxis() string
GetEndAxis returns the bottom right cell reference of merged range, for example: D4.
Get picture cells
func (f *File) GetPictureCells(sheet string) ([]string, error)
GetPictureCells returns all picture cell references in a worksheet by a specific worksheet name.
Add comment
func (f *File) AddComment(sheet string, comment Comment) error
AddComment provides the method to add comments in a sheet by given worksheet index, cell and format set (such as author and text). Note that the max author length is 255 and the max text length is 32512. For example, add a comment in Sheet1!$A$3:
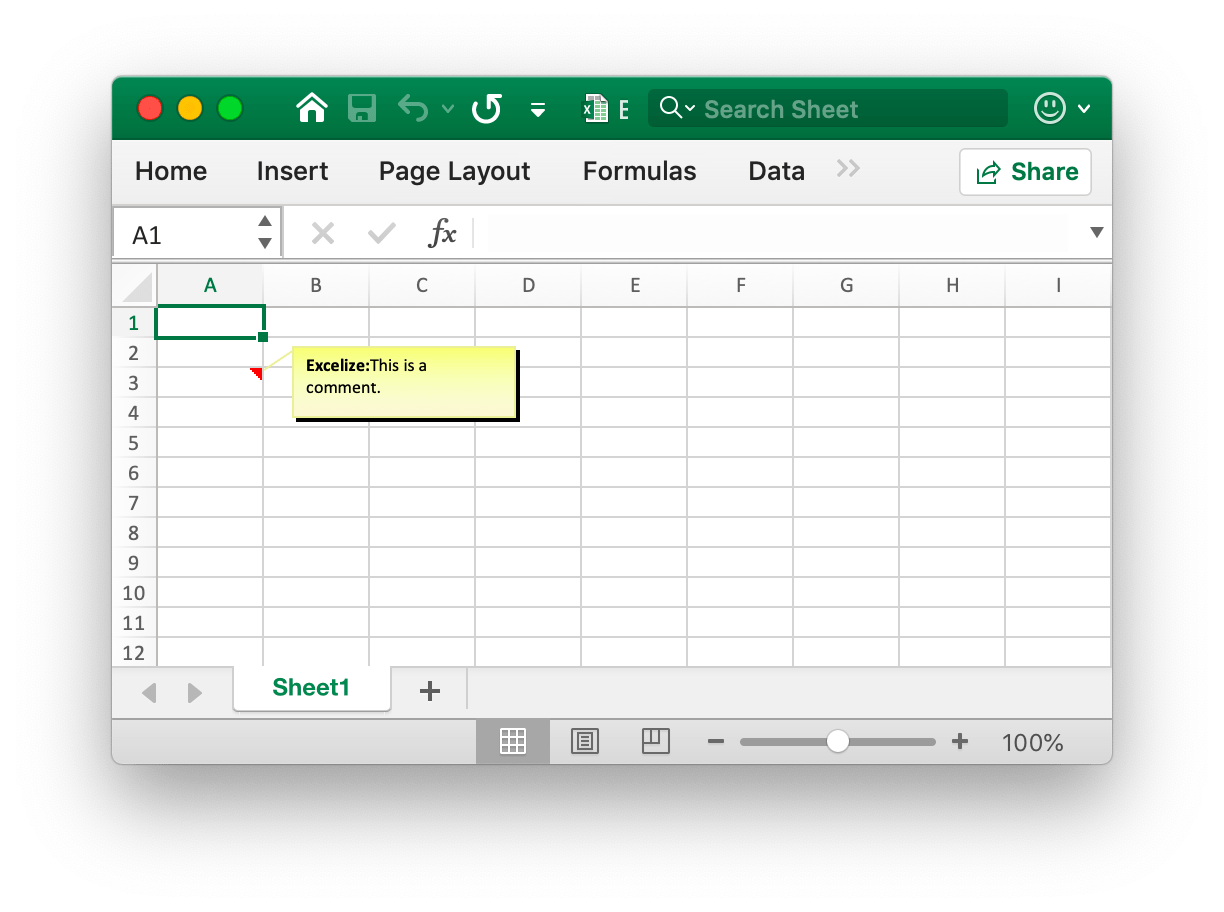
err := f.AddComment("Sheet1", excelize.Comment{
Cell: "A3",
Author: "Excelize",
Paragraph: []excelize.RichTextRun{
{Text: "Excelize: ", Font: &excelize.Font{Bold: true}},
{Text: "This is a comment."},
},
})
Get comment
func (f *File) GetComments(sheet string) ([]Comment, error)
GetComments retrieves all comments in a worksheet by given worksheet name.
Delete comment
func (f *File) DeleteComment(sheet, cell string) error
DeleteComment provides the method to delete comment in a sheet by given worksheet name. For example, delete the comment in Sheet1!$A$30:
err := f.DeleteComment("Sheet1", "A30")
Add ignored errors
func (f *File) AddIgnoredErrors(sheet, rangeRef string, ignoredErrorsType IgnoredErrorsType) error
AddIgnoredErrors provides the method to ignored error for a range of cells. For example: ignore "number stored as text" error on Sheet1 for range of cells D15 C18:D19:
err := f.AddIgnoredErrors("Sheet1", "D15 C18:D19", excelize.IgnoredErrorsNumberStoredAsText)
Set cell formula
func (f *File) SetCellFormula(sheet, cell, formula string, opts ...FormulaOpts) error
SetCellFormula provides a function to set the formula on the cell is taken according to the given worksheet name and cell formula settings. The result of the formula cell can be calculated when the worksheet is opened by the Office Excel application or can be using the CalcCellValue function also can get the calculated cell value. If the Excel application doesn't calculate the formula automatically when the workbook has been opened, please call UpdateLinkedValue after setting the cell formula functions.
- Example 1, set normal formula
=SUM(A1,B1)for the cellA3onSheet1:
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "A3", "SUM(A1,B1)")
- Example 2, set one-dimensional vertical constant array (column array) formula
1;2;3for the cellA3onSheet1:
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "A3", "{1;2;3}")
- Example 3, set one-dimensional horizontal constant array (row array) formula
"a","b","c"for the cellA3onSheet1:
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "A3", "{\"a\",\"b\",\"c\"}")
- Example 4, set two-dimensional constant array formula
{1,2;"a","b"}for the cellA3onSheet1:
formulaType, ref := excelize.STCellFormulaTypeArray, "A3:A3"
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "A3", "{1,2;\"a\",\"b\"}",
excelize.FormulaOpts{Ref: &ref, Type: &formulaType})
- Example 5, set range array formula
A1:A2for the cellA3onSheet1:
formulaType, ref := excelize.STCellFormulaTypeArray, "A3:A3"
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "A3", "A1:A2",
excelize.FormulaOpts{Ref: &ref, Type: &formulaType})
- Example 6, set shared formula
=A1+B1for the cellsC1:C5onSheet1,C1is the master cell:
formulaType, ref := excelize.STCellFormulaTypeShared, "C1:C5"
err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "C1", "A1+B1",
excelize.FormulaOpts{Ref: &ref, Type: &formulaType})
- Example 7, set table formula
=SUM(Table1[[A]:[B]])for the cellC2onSheet1:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
for idx, row := range [][]interface{}{{"A", "B", "C"}, {1, 2}} {
if err := f.SetSheetRow("Sheet1", fmt.Sprintf("A%d", idx+1), &row); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
}
if err := f.AddTable("Sheet1",
&excelize.Table{
Range: "A1:C2",
Name: "Table1",
StyleName: "TableStyleMedium2",
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
formulaType := excelize.STCellFormulaTypeDataTable
if err := f.SetCellFormula("Sheet1", "C2", "SUM(Table1[[A]:[B]])",
excelize.FormulaOpts{Type: &formulaType}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err := f.SaveAs("Book1.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
Get cell formula
func (f *File) GetCellFormula(sheet, cell string) (string, error)
GetCellFormula provides a function to get formula from cell by given worksheet name and cell reference in spreadsheet.
Calculate cell value
func (f *File) CalcCellValue(sheet, cell string, opts ...Options) (string, error)
CalcCellValue provides a function to get calculated cell value. This feature is currently in working processing. Iterative calculation, implicit intersection, explicit intersection, array formula, table formula and some other formulas are not supported currently.
Supported formulas:
| Function name | Description |
|---|---|
| ABS | Returns the absolute value of a number |
| ACCRINT | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest |
| ACCRINTM | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
| ACOS | Returns the arccosine of a number |
| ACOSH | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| ACOT | Returns the arccotangent of a number |
| ACOTH | Returns the hyperbolic arccotangent of a number |
| AGGREGATE | Returns an aggregate in a list or database |
| ADDRESS | Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet |
| AMORDEGRC | Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient |
| AMORLINC | Returns the depreciation for each accounting period |
| AND | Returns TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE |
| ARABIC | Converts a Roman number to Arabic, as a number |
| ARRAYTOTEXT | Returns an array of text values from any specified range |
| ASIN | Returns the arcsine of a number |
| ASINH | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
| ATAN | Returns the arctangent of a number |
| ATAN2 | Returns the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates |
| ATANH | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| AVEDEV | Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean |
| AVERAGE | Returns the average of its arguments |
| AVERAGEA | Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| AVERAGEIF | Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria |
| AVERAGEIFS | Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all cells that meet multiple criteria. |
| BASE | Converts a number into a text representation with the given radix (base) |
| BESSELI | Returns the modified Bessel function In(x) |
| BESSELJ | Returns the Bessel function Jn(x) |
| BESSELK | Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x) |
| BESSELY | Returns the Bessel function Yn(x) |
| BETADIST | Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
| BETA.DIST | Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
| BETAINV | Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
| BETA.INV | Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
| BIN2DEC | Converts a binary number to decimal |
| BIN2HEX | Converts a binary number to hexadecimal |
| BIN2OCT | Converts a binary number to octal |
| BINOMDIST | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| BINOM.DIST | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| BINOM.DIST.RANGE | Returns the probability of a trial result using a binomial distribution |
| BINOM.INV | Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
| BITAND | Returns a 'Bitwise And' of two numbers |
| BITLSHIFT | Returns a value number shifted left by shift_amount bits |
| BITOR | Returns a bitwise OR of 2 numbers |
| BITRSHIFT | Returns a value number shifted right by shift_amount bits |
| BITXOR | Returns a bitwise 'Exclusive Or' of two numbers |
| CEILING | Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| CEILING.MATH | Rounds a number up, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| CEILING.PRECISE | Rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up. |
| CHAR | Returns the character specified by the code number |
| CHIDIST | Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHIINV | Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHITEST | Returns the test for independence |
| CHISQ.DIST | Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
| CHISQ.DIST.RT | Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHISQ.INV | Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
| CHISQ.INV.RT | Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHISQ.TEST | Returns the test for independence |
| CHOOSE | Chooses a value from a list of values |
| CLEAN | Removes all nonprintable characters from text |
| CODE | Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string |
| COLUMN | Returns the column number of a reference |
| COLUMNS | Returns the number of columns in a reference |
| COMBIN | Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects |
| COMBINA | Returns the number of combinations with repetitions for a given number of items |
| COMPLEX | Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number |
| CONCAT | Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings, but it doesn't provide the delimiter or IgnoreEmpty arguments. |
| CONCATENATE | Joins several text items into one text item |
| CONFIDENCE | Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
| CONFIDENCE.NORM | Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
| CONFIDENCE.T | Returns the confidence interval for a population mean, using a Student's t distribution |
| CONVERT | Converts a number from one measurement system to another |
| CORREL | Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets |
| COS | Returns the cosine of a number |
| COSH | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| COT | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| COTH | Returns the cotangent of an angle |
| COUNT | Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments |
| COUNTA | Counts how many values are in the list of arguments |
| COUNTBLANK | Counts the number of blank cells within a range |
| COUNTIF | Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria |
| COUNTIFS | Counts the number of cells within a range that meet multiple criteria |
| COUPDAYBS | Returns the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date |
| COUPDAYS | Returns the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date |
| COUPDAYSNC | Returns the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date |
| COUPNCD | Returns the next coupon date after the settlement date |
| COUPNUM | Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date |
| COUPPCD | Returns the previous coupon date before the settlement date |
| COVAR | Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
| COVARIANCE.P | Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
| COVARIANCE.S | Returns the sample covariance, the average of the products deviations for each data point pair in two data sets |
| CRITBINOM | Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
| CSC | Returns the cosecant of an angle |
| CSCH | Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of an angle |
| CUMIPMT | Returns the cumulative interest paid between two periods |
| CUMPRINC | Returns the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods |
| DATE | Returns the serial number of a particular date |
| DATEDIF | Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age. |
| DATEVALUE | Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
| DAVERAGE | Returns the average of selected database entries |
| DAY | Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
| DAYS | Returns the number of days between two dates |
| DAYS360 | Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
| DB | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the fixed-declining balance method |
| DCOUNT | Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database |
| DCOUNTA | Counts non blank cells in a database |
| DDB | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the double-declining balance method or some other method that you specify |
| DEC2BIN | Converts a decimal number to binary |
| DEC2HEX | Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal |
| DEC2OCT | Converts a decimal number to octal |
| DECIMAL | Converts a text representation of a number in a given base into a decimal number |
| DEGREES | Converts radians to degrees |
| DELTA | Tests whether two values are equal |
| DEVSQ | Returns the sum of squares of deviations |
| DGET | Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified criteria |
| DISC | Returns the discount rate for a security |
| DMAX | Returns the maximum value from selected database entries |
| DMIN | Returns the minimum value from selected database entries |
| DOLLAR | Converts a number to text using currency format, with the decimals rounded to the number of places you specify |
| DOLLARDE | Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number |
| DOLLARFR | Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction |
| DPRODUCT | Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database |
| DSTDEV | Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries |
| DSTDEVP | Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries |
| DSUM | Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria |
| DURATION | Returns the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments |
| DVAR | Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries |
| DVARP | Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries |
| EDATE | Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
| EFFECT | Returns the effective annual interest rate |
| ENCODEURL | Returns a URL-encoded string |
| EOMONTH | Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
| ERF | Returns the error function |
| ERF.PRECISE | Returns the error function |
| ERFC | Returns the complementary error function |
| ERFC.PRECISE | Returns the complementary ERF function integrated between x and infinity |
| ERROR.TYPE | Returns a number corresponding to an error type |
| EUROCONVERT | Converts a number to euros, converts a number from euros to a euro member currency, or converts a number from one euro member currency to another by using the euro as an intermediary (triangulation). |
| EVEN | Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
| EXACT | Checks to see if two text values are identical |
| EXP | Returns e raised to the power of a given number |
| EXPON.DIST | Returns the exponential distribution |
| EXPONDIST | Returns the exponential distribution |
| FACT | Returns the factorial of a number |
| FACTDOUBLE | Returns the double factorial of a number |
| FALSE | Returns the logical value FALSE |
| F.DIST | Returns the F probability distribution |
| FDIST | Returns the F probability distribution |
| F.DIST.RT | Returns the F probability distribution |
| FIND | Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
| FINDB | Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
| F.INV | Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
| F.INV.RT | Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
| FINV | Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
| FISHER | Returns the Fisher transformation |
| FISHERINV | Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation |
| FIXED | Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals |
| FLOOR | Rounds a number down, toward zero |
| FLOOR.MATH | Rounds a number down, to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| FLOOR.PRECISE | Rounds a number the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. Regardless of the sign of the number, the number is rounded up |
| FORECAST | Returns a value along a linear trend |
| FORECAST.LINEAR | Returns a value along a linear trend |
| FORMULATEXT | Returns the formula at the given reference as text |
| FREQUENCY | Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array |
| F.TEST | Returns the result of an F-test |
| FTEST | Returns the result of an F-test |
| FV | Returns the future value of an investment |
| FVSCHEDULE | Returns the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates |
| GAMMA | Returns the Gamma function value |
| GAMMA.DIST | Returns the gamma distribution |
| GAMMADIST | Returns the gamma distribution |
| GAMMA.INV | Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
| GAMMAINV | Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
| GAMMALN | Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
| GAMMALN.PRECISE | Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
| GAUSS | Returns 0.5 less than the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| GCD | Returns the greatest common divisor |
| GEOMEAN | Returns the geometric mean |
| GESTEP | Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value |
| GROWTH | Returns values along an exponential trend |
| HARMEAN | Returns the harmonic mean |
| HEX2BIN | Converts a hexadecimal number to binary |
| HEX2DEC | Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal |
| HEX2OCT | Converts a hexadecimal number to octal |
| HLOOKUP | Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell |
| HOUR | Converts a serial number to an hour |
| HYPERLINK | Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet |
| HYPGEOM.DIST | Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
| HYPGEOMDIST | Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
| IF | Specifies a logical test to perform |
| IFERROR | Returns a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, returns the result of the formula |
| IFNA | Returns the value you specify if the expression resolves to #N/A, otherwise returns the result of the expression |
| IFS | Checks whether one or more conditions are met and returns a value that corresponds to the first TRUE condition. |
| IMABS | Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number |
| IMAGINARY | Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number |
| IMARGUMENT | Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians |
| IMCONJUGATE | Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number |
| IMCOS | Returns the cosine of a complex number |
| IMCOSH | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a complex number |
| IMCOT | Returns the cotangent of a complex number |
| IMCSC | Returns the cosecant of a complex number |
| IMCSCH | Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of a complex number |
| IMDIV | Returns the quotient of two complex numbers |
| IMEXP | Returns the exponential of a complex number |
| IMLN | Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number |
| IMLOG10 | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number |
| IMLOG2 | Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number |
| IMPOWER | Returns a complex number raised to an integer power |
| IMPRODUCT | Returns the product of complex numbers |
| IMREAL | Returns the real coefficient of a complex number |
| IMSEC | Returns the secant of a complex number |
| IMSECH | Returns the hyperbolic secant of a complex number |
| IMSIN | Returns the sine of a complex number |
| IMSINH | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a complex number |
| IMSQRT | Returns the square root of a complex number |
| IMSUB | Returns the difference between two complex numbers |
| IMSUM | Returns the sum of complex numbers |
| IMTAN | Returns the tangent of a complex number |
| INDEX | Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array |
| INDIRECT | Returns a reference indicated by a text value |
| INT | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer |
| INTERCEPT | Returns the intercept of the linear regression line |
| INTRATE | Returns the interest rate for a fully invested security |
| IPMT | Returns the interest payment for an investment for a given period |
| IRR | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| ISBLANK | Returns TRUE if the value is blank |
| ISERR | Returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A |
| ISERROR | Returns TRUE if the value is any error value |
| ISEVEN | Returns TRUE if the number is even |
| ISFORMULA | Returns TRUE if there is a reference to a cell that contains a formula |
| ISLOGICAL | Returns TRUE if the value is a logical value |
| ISNA | Returns TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value |
| ISNONTEXT | Returns TRUE if the value is not text |
| ISNUMBER | Returns TRUE if the value is a number |
| ISODD | Returns TRUE if the number is odd |
| ISREF | Returns TRUE if the value is a reference |
| ISTEXT | Returns TRUE if the value is text |
| ISO.CEILING | Returns a number that is rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| ISOWEEKNUM | Returns the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date |
| ISPMT | Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment |
| KURT | Returns the kurtosis of a data set |
| LARGE | Returns the k-th largest value in a data set |
| LCM | Returns the least common multiple |
| LEFT | Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
| LEFTB | Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
| LEN | Returns the number of characters in a text string |
| LENB | Returns the number of characters in a text string |
| LN | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
| LOG10 | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
| LOGINV | Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution |
| LOGNORM.DIST | Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
| LOGNORMDIST | Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
| LOGNORM.INV | Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution |
| LOOKUP | Looks up values in a vector or array |
| LOWER | Converts text to lowercase |
| MATCH | Looks up values in a reference or array |
| MAX | Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments |
| MAXA | Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| MAXIFS | Returns the maximum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria |
| MDETERM | Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
| MDURATION | Returns the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100 |
| MEDIAN | Returns the median of the given numbers |
| MID | Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
| MIDB | Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
| MIN | Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments |
| MINIFS | Returns the minimum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria. |
| MINA | Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| MINUTE | Converts a serial number to a minute |
| MINVERSE | Returns the matrix inverse of an array |
| MIRR | Returns the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates |
| MMULT | Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
| MOD | Returns the remainder from division |
| MODE | Returns the most common value in a data set |
| MODE.MULT | Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring, or repetitive values in an array or range of data |
| MODE.SNGL | Returns the most common value in a data set |
| MONTH | Converts a serial number to a month |
| MROUND | Returns a number rounded to the desired multiple |
| MULTINOMIAL | Returns the multinomial of a set of numbers |
| MUNIT | Returns the unit matrix or the specified dimension |
| N | Returns a value converted to a number |
| NA | Returns the error value #N/A |
| NEGBINOM.DIST | Returns the negative binomial distribution |
| NEGBINOMDIST | Returns the negative binomial distribution |
| NETWORKDAYS | Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL | Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
| NOMINAL | Returns the annual nominal interest rate |
| NORM.DIST | Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
| NORMDIST | Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
| NORMINV | Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
| NORM.INV | Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
| NORM.S.DIST | Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| NORMSDIST | Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| NORM.S.INV | Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| NORMSINV | Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
| NOT | Reverses the logic of its argument |
| NOW | Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
| NPER | Returns the number of periods for an investment |
| NPV | Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate |
| OCT2BIN | Converts an octal number to binary |
| OCT2DEC | Converts an octal number to decimal |
| OCT2HEX | Converts an octal number to hexadecimal |
| ODD | Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
| ODDFPRICE | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period |
| ODDFYIELD | Returns the yield of a security with an odd first period |
| ODDLPRICE | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period |
| ODDLYIELD | Returns the yield of a security with an odd last period |
| OR | Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE |
| PDURATION | Returns the number of periods required by an investment to reach a specified value |
| PEARSON | Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
| PERCENTILE.EXC | Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive |
| PERCENTILE.INC | Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
| PERCENTILE | Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
| PERCENTRANK.EXC | Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set |
| PERCENTRANK.INC | Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
| PERCENTRANK | Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
| PERMUT | Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects |
| PERMUTATIONA | Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total objects |
| PHI | Returns the value of the density function for a standard normal distribution |
| PI | Returns the value of pi |
| PMT | Returns the periodic payment for an annuity |
| POISSON.DIST | Returns the Poisson distribution |
| POISSON | Returns the Poisson distribution |
| POWER | Returns the result of a number raised to a power |
| PPMT | Returns the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period |
| PRICE | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest |
| PRICEDISC | Returns the price per $100 face value of a discounted security |
| PRICEMAT | Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity |
| PROB | Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits |
| PRODUCT | Multiplies its arguments |
| PROPER | Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value |
| PV | Returns the present value of an investment |
| QUARTILE | Returns the quartile of a data set |
| QUARTILE.EXC | Returns the quartile of the data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive |
| QUARTILE.INC | Returns the quartile of a data set |
| QUOTIENT | Returns the integer portion of a division |
| RADIANS | Converts degrees to radians |
| RAND | Returns a random number between 0 and 1 |
| RANDBETWEEN | Returns a random number between the numbers you specify |
| RANK.EQ | Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
| RANK | Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
| RATE | Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity |
| RECEIVED | Returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security |
| REPLACE | Replaces characters within text |
| REPLACEB | Replaces characters within text |
| REPT | Repeats text a given number of times |
| RIGHT | Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
| RIGHTB | Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
| ROMAN | Converts an arabic numeral to roman, as text |
| ROUND | Rounds a number to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDDOWN | Rounds a number down, toward zero |
| ROUNDUP | Rounds a number up, away from zero |
| ROW | Returns the row number of a reference |
| ROWS | Returns the number of rows in a reference |
| RRI | Returns an equivalent interest rate for the growth of an investment |
| RSQ | Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
| SEARCH | Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
| SEARCHB | Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
| SEC | Returns the secant of an angle |
| SECH | Returns the hyperbolic secant of an angle |
| SECOND | Converts a serial number to a second |
| SERIESSUM | Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula |
| SHEET | Returns the sheet number of the referenced sheet |
| SHEETS | Returns the number of sheets in a reference |
| SIGN | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIN | Returns the sine of the given angle |
| SINH | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
| SKEW | Returns the skewness of a distribution |
| SKEW.P | Returns the skewness of a distribution based on a population: a characterization of the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean |
| SLN | Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period |
| SLOPE | Returns the slope of the linear regression line |
| SMALL | Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set |
| SQRT | Returns a positive square root |
| SQRTPI | Returns the square root of (number * pi) |
| STANDARDIZE | Returns a normalized value |
| STDEV | Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
| STDEV.P | Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
| STDEV.S | Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
| STDEVA | Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| STDEVP | Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
| STDEVPA | Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| STEYX | Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression |
| SUBSTITUTE | Substitutes new text for old text in a text string |
| SUBTOTAL | Returns a subtotal in a list or database |
| SUM | Adds its arguments |
| SUMIF | Adds the cells specified by a given criteria |
| SUMIFS | Adds the cells in a range that meet multiple criteria |
| SUMPRODUCT | Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array components |
| SUMSQ | Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments |
| SUMX2MY2 | Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
| SUMX2PY2 | Returns the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
| SUMXMY2 | Returns the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays |
| SWITCH | Evaluates an expression against a list of values and returns the result corresponding to the first matching value. If there is no match, an optional default value may be returned. |
| SYD | Returns the sum-of-years' digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period |
| T | Converts its arguments to text |
| TAN | Returns the tangent of a number |
| TANH | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| TBILLEQ | Returns the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill |
| TBILLPRICE | Returns the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill |
| TBILLYIELD | Returns the yield for a Treasury bill |
| T.DIST | Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution |
| T.DIST.2T | Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution |
| T.DIST.RT | Returns the Student's t-distribution |
| TDIST | Returns the Student's t-distribution |
| TEXT | Formats a number and converts it to text |
| TEXTAFTER | Returns text that occurs after given character or string |
| TEXTBEFORE | Returns text that occurs before a given character or string |
| TEXTJOIN | Combines the text from multiple ranges and/or strings |
| TIME | Returns the serial number of a particular time |
| TIMEVALUE | Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
| T.INV | Returns the t-value of the Student's t-distribution as a function of the probability and the degrees of freedom |
| T.INV.2T | Returns the inverse of the Student's t-distribution |
| TINV | Returns the inverse of the Student's t-distribution |
| TODAY | Returns the serial number of today's date |
| TRANSPOSE | Returns the transpose of an array |
| TREND | Returns values along a linear trend |
| TRIM | Removes spaces from text |
| TRIMMEAN | Returns the mean of the interior of a data set |
| TRUE | Returns the logical value TRUE |
| TRUNC | Truncates a number to an integer |
| T.TEST | Returns the probability associated with a Student's t-test |
| TTEST | Returns the probability associated with a Student's t-test |
| TYPE | Returns a number indicating the data type of a value |
| UNICHAR | Returns the Unicode character that is references by the given numeric value |
| UNICODE | Returns the number (code point) that corresponds to the first character of the text |
| UPPER | Converts text to uppercase |
| VALUE | Converts a text argument to a number |
| VALUETOTEXT | Returns text from any specified value |
| VAR | Estimates variance based on a sample |
| VAR.P | Calculates variance based on the entire population |
| VAR.S | Estimates variance based on a sample |
| VARA | Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| VARP | Calculates variance based on the entire population |
| VARPA | Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| VDB | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period by using a declining balance method |
| VLOOKUP | Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell |
| WEEKDAY | Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
| WEEKNUM | Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
| WEIBULL | Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
| WEIBULL.DIST | Returns the Weibull distribution |
| WORKDAY | Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
| WORKDAY.INTL | Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
| XIRR | Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
| XLOOKUP | Searches a range or an array, and returns an item corresponding to the first match it finds. If a match doesn't exist, then XLOOKUP can return the closest (approximate) match. |
| XNPV | Returns the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
| XOR | Returns a logical exclusive OR of all arguments |
| YEAR | Converts a serial number to a year |
| YEARFRAC | Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
| YIELD | Returns the yield on a security that pays periodic interest |
| YIELDDISC | Returns the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill |
| YIELDMAT | Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity |
| Z.TEST | Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
| ZTEST | Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |